Laparoscopic Surgery
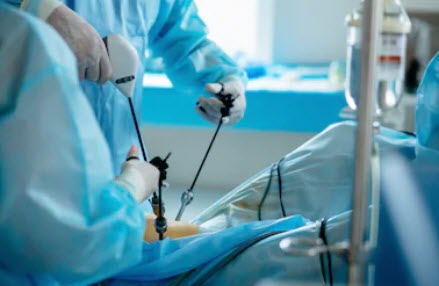
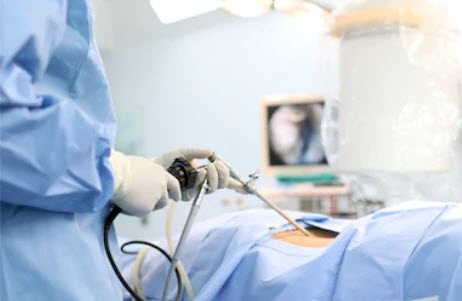
Also called keyhole surgery. Only small incisions are required. As a result it is a minimally invasive procedure. An instrument called a laparoscope is used to examine the abdominal organs which is a thin long tube with a high intensity light and high resolution camera.
One incision is used to deliver carbon dioxide into the abdomen. This is done using a small tube called a cannula. Inflate the abdomen with carbon dioxide gas allows the surgeons to view the organs in the abdomen much easier.
Another incision is used for the insertion of a laparoscope that consists of a light within a thin tube and camera which displays the abdomen on a monitor to guide the surgeon in removing and/or repairing tissue.
Laparoscopic surgery is advantageous over traditional surgery as it results in smaller scarring at the incision sites, possibly less internal scarring, and a faster post surgery recovery period.
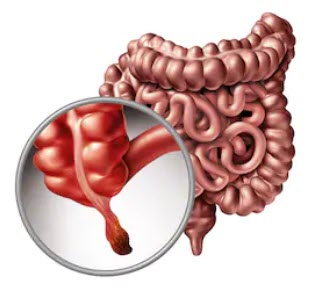
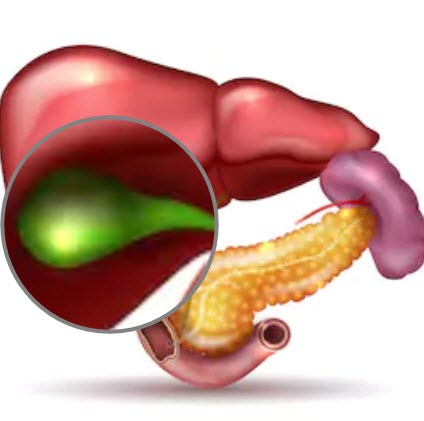
Appendix
Laparoscopic appendectomy is the removal of the appendix using three small incisions in the abdomen.
Gallbladder
Laparoscopic gallbladder surgery involves the removal of the gallbladder and gallstones through minimally invasive surgery with small incisions in the abdomen.
Inguinal, Femoral & Spigelian Hernia
Laparoscopic hernia repair involves two to four small incisions to use a laparoscope and cannula for the hernia repair.
Spleen
Laparoscopic splenectomy is the removal of the spleen through small incisions.
